Amplifiers are essential for the correct operation of all communication systems. In addition to the requirements for their linear operation, there is also a requirement for efficiency. Usually, efficient amplifiers are not necessarily linear and the process of linearization is usually performed using a Digital Pre-Distorter (DPD) on an efficient amplifier, which distorts the input signal in a specific way to yield a linear output. There are several amplifier efficiency enhancement techniques, however, the Doherty amplifier, introduced in 1936 [1], has been the mainstay in the telecommunications industry due to its inherent simplicity and efficiency.
This paper-review describes the historical aspect of the Doherty approach to the power amplifier design introduced in 1936 and modern trends in Doherty amplifier design techniques using multistage and asymmetric multi-way architectures. To increase efficiency over the power backoff range, the switch-mode Class E, conventional Class F, or inverse Class F operation mode by controlling the second and third harmonics can be used in the load network. The Doherty amplifier with a series connected load, inverted and dual-mode Doherty architectures are also described and discussed. Finally, examples of the lumped Doherty amplifier implemented in monolithic microwave integrated circuits and broadband capability of the two-stage Doherty amplifier are given.
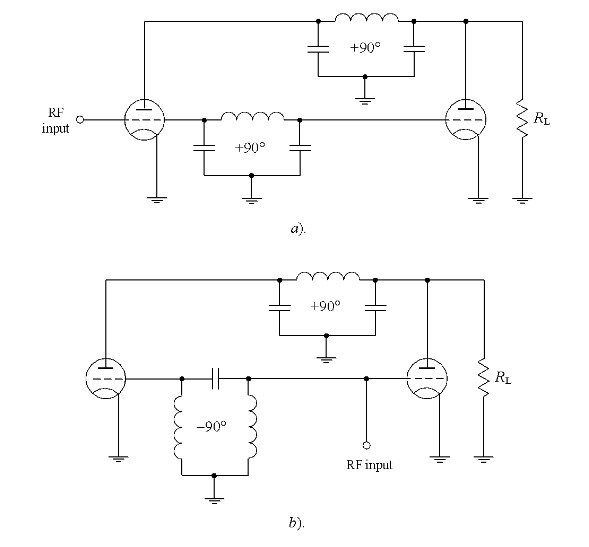
[1] W. H. Doherty (September 1936). “A New High Efficiency Power Amplifier for Modulated Waves”. Proceedings of the IRE. 24 (9): 1163–1182. doi:10.1109/JRPROC.1936.228468.
Leave a Reply