The interest in reconfigurable RF devices has been the motivation for the current gradual development of various voltage tuneable materials. Liquid Crystals (LCs) are promising tuneable materials as their dielectric properties can be controlled under an external bias field with negligible power consumption. Several nematic LC-based microwave devices have been reported in the literature, such as tuneable microstrip antennas, variable delay lines, phase shifters, and steerable reflect arrays.
Nematic LCs, which are largely used in display technology, are liquid anisotropic materials that exhibit a variation of relative dielectric permittivity when subjected to an external electric or magnetic field. These materials are relatively cheap and respond to low voltages, which is an advantage, compared with ferroelectrics requiring high operating voltages. A number of factors influence the choice of an LC for an RF application. Improved and specialized LCs offering temperature stability, with large dielectric anisotropy (r), are being developed for some RF devices. However, it is believed that the main applications of nematic LCs in RF will be in and beyond millimeter-wave (mm-wave) frequencies where a small change in the director orientation significantly affects the wavelength and wave impedance. Therefore, characterization of the dielectric properties of the LC in mm-wave frequencies is essential.
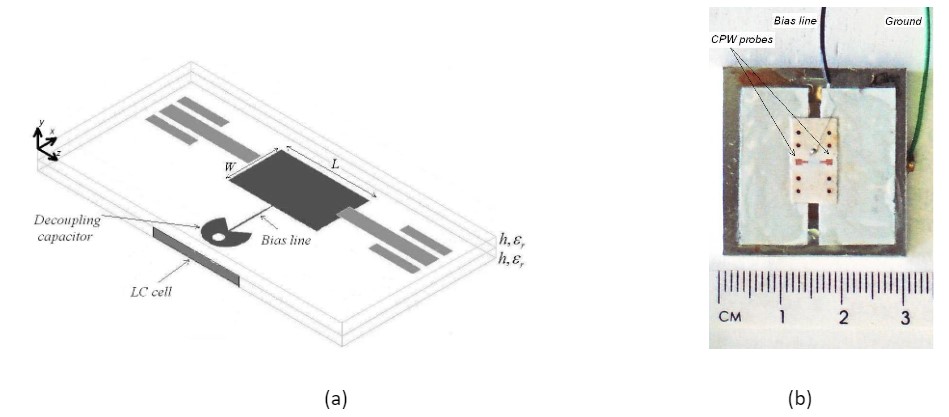
This paper presents a new resonant technique-based method for measuring the dielectric constants of nematic LC at 40 GHz. For this purpose, a patch resonator is designed with a cavity formed underneath it to accommodate the LC as a dielectric substrate between the patch and the ground plane, Fig. 1. A useful feature of the presented characterization method lies with the direct application of the electric field for the alignment of LC molecules. This is achieved by using a low frequency AC voltage signal which allows partial switching of the LC, useful in finding precise values of the anisotropic dielectric constant at any given bias voltage. The measurements of dielectric constants and dielectric constant anisotropy of a nematic LC commonly known as E7 are conducted, and the results in very close agreement with the values reported in the literature.
Leave a Reply