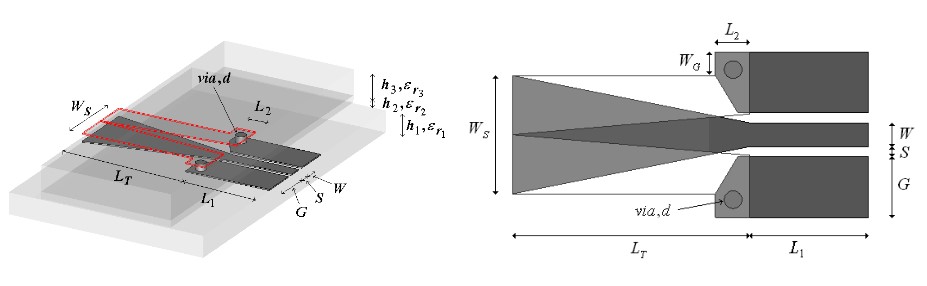
The coplanar waveguide (CPW) and the microstrip line are the two most commonly used transmission lines in millimeter and sub-millimeter wave circuits since they are compact and easy to fabricate. The width of the ground conductors of the CPW is always finite in practice, in which case the structure is sometimes referred to as Finite Ground CPW (FGCPW). Highly integrated microwave circuits often comprise a combination of CPW and microstrip lines, thus requiring suitable low-loss interconnections (transitions) between these two lines.
Even though the CPW or FGCPW to the microstrip line transitions are important and well established, in certain RF system-on-chip applications, a low-loss low-radiation transition is required to connect the CPW or FGCPW to the microstrip line with a finite ground plane. When the width of the ground plane is the same as the strip line, the resulting structure is, in effect, a balanced strip line.
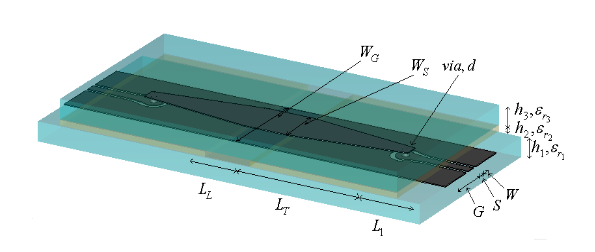
This paper presents, for the first time a taper from a FGCPW to the balanced stripline. The transition is wide-band and is designed to operate within the frequency range DC to 65 GHz. The transition is partly tapered, multilayered and consists of two via interconnects. The measurements of the transition show a good agreement with simulations, with a maximum disagreement of 0.7 dB at 58 GHz for |S21| which can be due to the fabrication process. The maximum measured and simulated insertion losses of the transition are about 2.1 dB, part of which is due to some surface wave radiation.
This transition can find its use in a variety of MMIC applications, such as RF systems-on-chip.
Leave a Reply