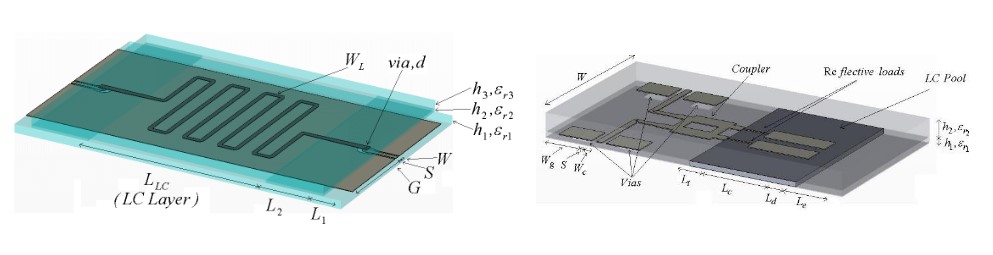
Liquid Crystals (LCs) are promising dielectric media for a range of mm-wave devices. Their main advantage stems from the fact that their dielectric properties can be externally controlled by an electric or magnetic field. As such, LCs have already found some uses in the design of mm-wave devices such as tunable microstrip line phase shifters [1-2]. In [1-2], the phase shifters are simply made of a length of a microstrip line including a LC substrate. Therefore, the amount of the phase shift is dependent on the length of the microstrip line exposed to the LC. This becomes highly impractical when high values of phase shift are required as long length microstrip lines are needed. For example, in [2] the 50 mm length of the line achieves a differential phase shift of about 90 degrees at 24 GHz, when the LC mixture is K15.
Preliminary structures and performance results of two different 60 GHz band planar phase shifters using liquid crystal (LC) are presented in this paper. The first phase shifter is based on a meandered microstrip line structure with the conductor pattern exposed to a layer of a nematic LC, while the second phase shifter is Reflection-Type Phase Shifter (RTPS) whose tunable reflective loads are formed on a nematic LC substrate. The LC mixture used in these two phase shifters is E7 with a low temperature coefficient over a wide range of temperatures. In both phase shifters, the LC is biased through a variable low voltage external source allowing for the control of the dielectric constant of the LC. To facilitate the on-wafer measurement and the application of the electric field to the LC, a broadband transition from the microstrip line to the CPW is developed and used in both phase shifters. The best figure of merit of the meandered line phase shifter, 20.8° dB, occurs at 60.7 GHz coinciding with a differential phase shift of 243 degrees, while the RTPS achieves a maximum figure of merit, 12.3° dB, at 61.31 GHz corresponding to a differential phase shift of 170 degrees.
[1] N. Martin, P. Laurent, G. Prigent, P. Gelin and F. Huret, “ Improvement of an inverted microstrip-line microwave phase-shifter using liquid crystal”, 33rd European Microwave Conference (EuMC 2003), pp. 1417-1420, 2003, Munich, Germany.
[2] S. Mueller, P. Scheele, C. Weil, M. Wittek, C. Hock and R. Jakoby, “Tunable passive phase shifter for microwave applications using highly anisotropic liquid crystals”, IEEE, MTT-S Int. Microwave Symp.Dig., pp. 1153- 1156, 2004.
Leave a Reply